Photo by Ernest Ojeh on Unsplash
Beyond the Plug
Understanding the Challenges and Opportunities in Electric Vehicle Charging
Electric vehicles (EVs) have been gaining popularity in recent years as a more sustainable and eco-friendly mode of transportation. However, as with any new technology, there are still some challenges that need to be addressed to make EVs more convenient and practical for everyday use. One of these challenges is the issue of EV charging protocols and current convention methods. In this article we will go through the current EV protocols, types of chargers, EV charging providers, current challenges and much more. Lets Dive in, Happy Reading.
EV Charging Protocols
There are several different protocols for EV charging, each with its advantages and disadvantages. The most common protocols are:
CHAdeMO - This is a Japanese standard that is used by many EV manufacturers, including Nissan and Mitsubishi. It uses a high-speed DC charging system that can deliver up to 62.5 kW of power, allowing for quick charging times.
CCS - This is a European standard that has been adopted by many automakers, including BMW, Volkswagen, and Audi. It can deliver up to 350 kW of power, which is much faster than CHAdeMO.
Tesla Supercharger - This is a proprietary charging system that is used by Tesla vehicles. It can deliver up to 250 kW of power and is currently the fastest charging system available.
AC Charging - This is a slower charging method that uses an AC current. It is often used for home charging or for slower public charging stations.

Current Convention Methods
Currently, several conventional methods for EV charging are widely used which include:
Public Charging Stations - There are many public charging stations available for EV owners to use. These can be found at shopping malls, airports, and other public areas. Some public charging stations are free, while others require payment.
Home Charging - Many EV owners choose to install a home charging station, which allows them to charge their vehicles overnight. This is often the most convenient and cost-effective method of charging.
Workplace Charging - Some employers offer workplace charging stations for their employees. This can be a great perk for EV owners who need to charge their vehicles during the workday.
Destination Charging - Some hotels, restaurants, and other destinations offer charging stations for their customers. This can be a great way to attract EV owners and provide a convenient service. Conclusion EV charging protocols and current convention methods are important considerations for anyone who is thinking about purchasing an EV. It is important to research the different protocols and charging methods to determine which one is best for your needs. Additionally, as the technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see even faster and more convenient charging options become available in the near future.
EV plug Types
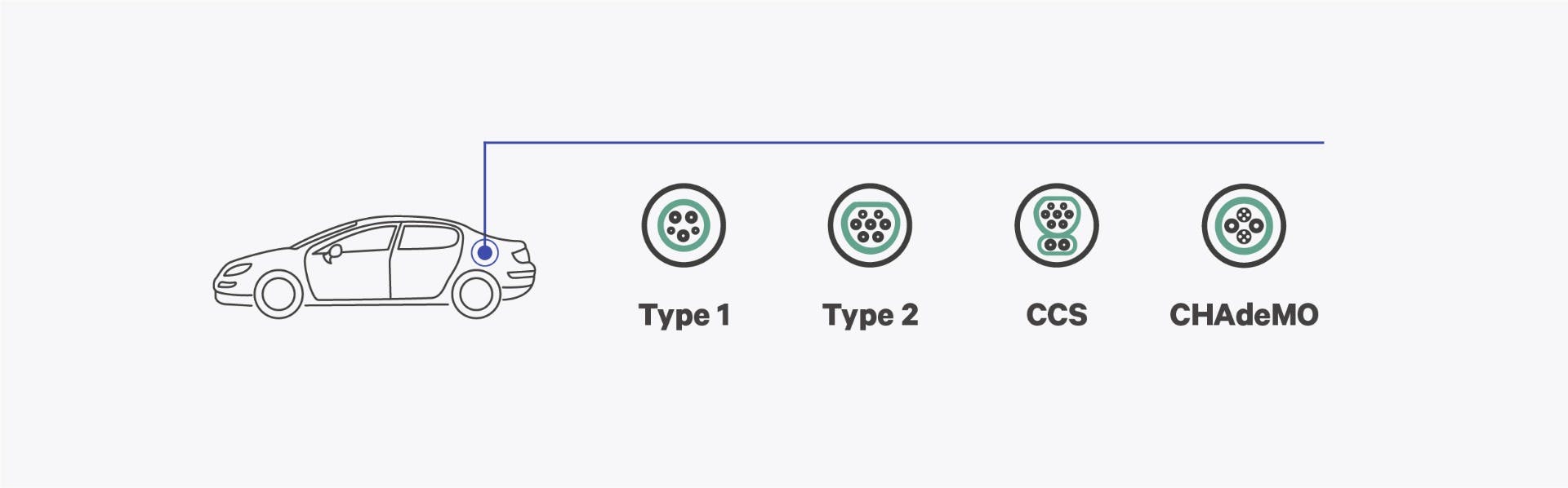
There are several plug types used for electric vehicle (EV) charging around the world. Here are some of the most common plug types with images:
Type 1 - This is the North American standard for EV charging, also known as the J1772 plug. It has five pins and is used for Level 1 and Level 2 charging.
Type 2 - This is the European standard for EV charging, also known as the Mennekes plug. It has seven pins and is used for both Level 1 and Level 2 charging.
CCS - This is the Combined Charging System, a standard developed by European and American automakers. It has nine pins and is used for both AC and DC charging.
CHAdeMO - This is a Japanese standard for DC fast charging. It has six pins and is used by many Asian automakers such as Nissan and Mitsubishi.
Tesla Supercharger - This is a proprietary charging system used by Tesla vehicles. It is compatible only with Tesla vehicles and has a unique charging port.
It is important to note that not all plug types are compatible with all EVs. Before using a charging station, it is important to check the compatibility of the plug type with your EV. Additionally, some charging stations may require an adapter to use certain plug types.
Major EV Providers
As electric vehicles (EVs) become increasingly popular, the number of EV charging providers around the world is also growing. Here are some of the major EV charging providers worldwide:
Tesla Supercharger - Tesla's proprietary charging network is one of the largest and fastest in the world. It currently has over 25,000 Superchargers across 41 countries.
ChargePoint - ChargePoint is one of the largest EV charging networks in North America, with over 115,000 charging ports across the US and Canada.
EVgo - EVgo is one of the largest public EV charging networks in the US, with over 800 fast-charging stations across 34 states.
Ionity - Ionity is a joint venture between several major automakers, including BMW, Daimler, Ford, and Volkswagen. It is focused on developing a high-speed charging network across Europe, with over 400 charging stations in 26 countries.
Fastned - Fastned is a Dutch company that operates a network of fast-charging stations across the Netherlands, Germany, and the UK. It currently has over 130 stations and plans to expand further across Europe.
Greenlots - Greenlots is a global provider of EV charging solutions, with operations in North America, Europe, and Asia. It provides both hardware and software solutions for EV charging, including residential and commercial charging solutions.
BP Chargemaster - BP Chargemaster is one of the largest EV charging providers in the UK, with over 7,000 charging points across the country. It provides both slow and fast charging solutions for residential, commercial, and public use.
Electrify America - Electrify America is a subsidiary of Volkswagen Group of America and operates a network of fast-charging stations across the US. It currently has over 600 charging stations across 45 states.
ABB - ABB is a Swiss-based multinational corporation that provides charging solutions for electric cars, buses, and trucks. It operates in over 100 countries and has installed over 14,000 DC fast chargers worldwide.
Enel X - Enel X is a global provider of energy solutions, including EV charging infrastructure. It operates a network of public charging stations across Italy, Spain, Romania, and Russia, and provides both hardware and software solutions for residential and commercial use. These are just a few of the many EV charging providers operating worldwide. As the demand for EVs grows, it is likely that we will see even more companies entering the EV charging market in the years to come.
Chargenode and Eways are two EV charging providers that operate in specific regions. Chargenode is a French company that provides charging solutions for EV fleets, such as taxis, buses, and delivery vehicles. Its charging stations are designed to be scalable and can charge multiple vehicles at once. Chargenode also provides software solutions for fleet management, charging management, and energy management. Eways is an Australian EV charging provider that focuses on providing charging solutions for commercial and residential customers. Its charging stations are designed to be easy to install and operate, and can be used for both Level 2 and DC fast charging. Eways also provides software solutions for charging management, payment processing, and remote monitoring. While both Chargenode and Eways are relatively smaller players in the EV charging market compared to some of the larger global providers, they are important in their respective regions and provide valuable solutions for specific customer segments.
Siemens is a multinational conglomerate that provides a wide range of products and services, including EV charging solutions. Siemens provides charging solutions for both residential and commercial customers, and offers a variety of charging stations, including AC and DC fast charging stations. One of Siemens' notable products is the VersiCharge AC charger, which is designed for residential and light commercial use. It offers Level 2 charging and is compatible with all EVs that use the J1772 standard. Siemens also offers DC fast charging solutions, such as the Sicharge D fast charger, which can charge an EV up to 80% in 30 minutes. Siemens' charging solutions are designed to be scalable and can be customized to fit the needs of individual customers. Siemens also provides software solutions for charging management, payment processing, and remote monitoring. Overall, Siemens is an important player in the EV charging market, with a strong reputation for providing high-quality and reliable charging solutions.
Current Challenges in EV World
Electric vehicle (EV) charging infrastructure has come a long way in recent years, but there are still challenges that need to be addressed to make EVs more practical and convenient for everyday use. Some of the current challenges faced by EV charging include:
Range anxiety - EV drivers often worry about running out of battery power before reaching their destination. This is especially true for longer trips that require multiple charging stops.
Lack of charging stations - Although there are many public charging stations available, there are still not enough to meet the needs of all EV drivers. In some areas, EV drivers may need to travel long distances to find a charging station.
Charging time - Even with fast charging options, EV charging can take longer than refueling a gas-powered vehicle. This can be inconvenient for drivers who need to get back on the road quickly.
Cost - The cost of installing and operating EV charging infrastructure can be high, which can deter some businesses and property owners from installing charging stations. Several improvements can be made to address these challenges and make EV charging more practical and convenient. Some of these include:
Improved battery technology - Improvements in battery technology can increase the range of EVs and reduce range anxiety. Additionally, faster charging times and longer battery life can make EVs more practical for everyday use.
Increased charging station availability - Expanding the number of charging stations available can help to address the issue of range anxiety and ensure that EV drivers can find a charging station when they need one. Governments and businesses can incentivize the installation of charging stations to help expand the charging network.
Faster charging times - Advancements in charging technology can reduce the amount of time it takes to charge an EV. For example, ultra-fast charging technology can deliver a full charge in just a few minutes, making charging times comparable to refueling a gas-powered vehicle.
Lower cost - As EVs become more popular, economies of scale can help to drive down the cost of EV charging infrastructure. Governments can also provide subsidies or tax incentives to encourage the installation of charging stations. In conclusion, while there are still challenges facing EV charging, advancements in battery technology and charging infrastructure are making EVs more practical and convenient for everyday use. By continuing to invest in and expand the charging network, governments and businesses can help to accelerate the adoption of EVs and reduce reliance on fossil fuels.
As technology continues to advance, we can expect to see even more innovation in the EV charging space. From wireless charging to high-speed charging stations, the future of EV charging is bright and full of possibility.
